Power of Rainwater: Collection, Storage, and Filtration Tips
As concerns about water scarcity and sustainability grow, many people are turning to alternative sources to meet their water needs. Rainwater harvesting is an age-old practice that has gained renewed interest in modern times. This blog post explores the benefits of rainwater, how to collect and store it safely, and tips for ensuring it's clean and drinkable through effective filtration.
The Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting
Sustainability: Rainwater is a renewable resource. Collecting it reduces reliance on municipal water supplies and groundwater.
Cost Savings: Harvesting rainwater can significantly lower water bills, especially in areas with high water costs.
Plant Health: Rainwater is naturally soft and free of chemicals like chlorine, making it ideal for watering plants.
Environmental Impact: Reducing runoff can minimize erosion and pollution in local waterways.
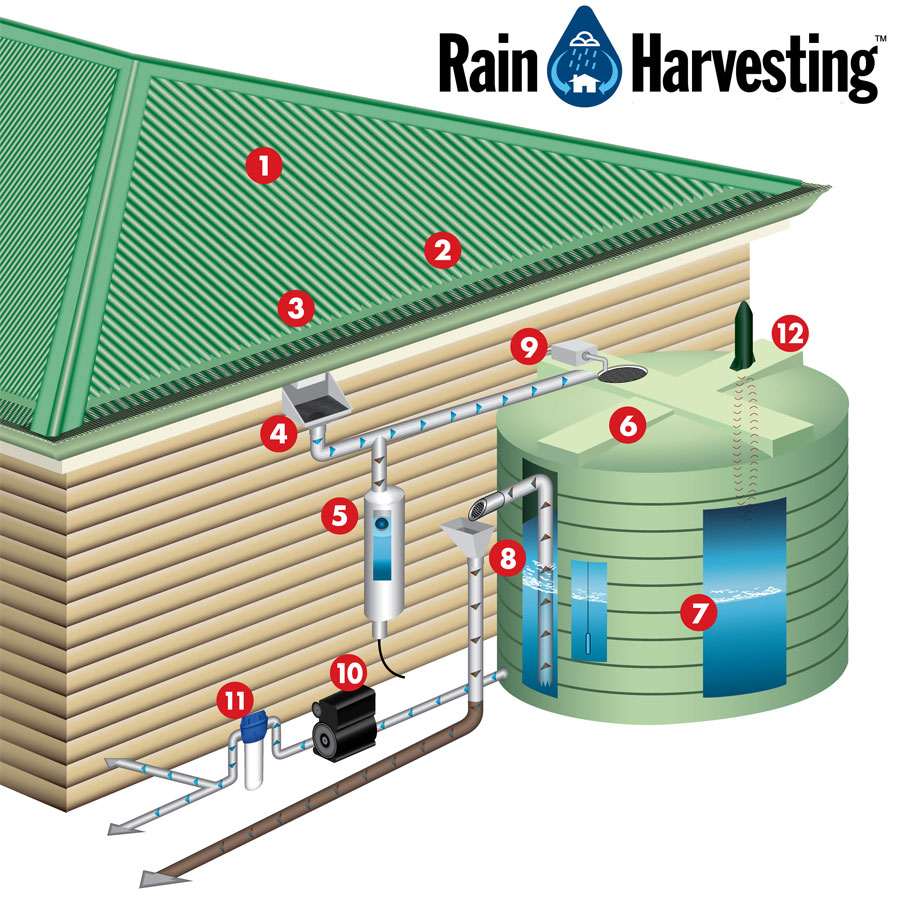
How to Collect Rainwater
Roof Catchment: Most rainwater harvesting systems start with a roof. Ensure your roof is made from safe materials (avoid asbestos and treated wood) to prevent contamination.
Gutters and Downspouts: Install gutters and downspouts to channel rainwater from the roof to your storage system. Clean them regularly to remove leaves and debris.
First Flush Diverter: This device helps divert the initial flow of water, which may contain contaminants from the roof, away from your storage tank.
Storage Containers: Choose food-grade materials for your rain barrels or tanks to prevent chemical leaching. Options include plastic, metal, and concrete containers.
How to Store Rainwater Safely
Choose the Right Location: Place your storage container on a stable, level surface, preferably in a shaded area to prevent algae growth.
Use a Lid: Always cover your storage container to keep out debris, insects, and animals.
Regular Maintenance: Clean your storage containers periodically to prevent buildup of dirt and contaminants.
Prevent Mosquito Breeding: Ensure your containers are sealed properly to prevent mosquitoes from laying eggs. Consider adding a layer of vegetable oil to the surface of the water to deter mosquitoes.
Tips for Filtering Rainwater
While rainwater is generally clean, it can still pick up contaminants from the collection surface and storage container. Here are some effective filtration methods:
Sediment Filters: Use a pre-filter to remove larger particles and sediments from the water. This can be a simple mesh filter or a more sophisticated cartridge filter.
Activated Carbon Filters: These filters remove organic compounds, chlorine, and other chemicals, improving the taste and odor of the water.
Ceramic Filters: Ceramic filters are effective at removing bacteria, protozoa, and other pathogens. They have tiny pores that trap contaminants while allowing water to pass through.
UV Purifiers: Ultraviolet (UV) purifiers use UV light to kill bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms. This method is effective and doesn't add chemicals to the water.
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems: RO systems force water through a semi-permeable membrane, removing a wide range of contaminants, including heavy metals and pathogens. This method is more expensive but provides high-quality drinking water.
Rainwater harvesting is a practical and eco-friendly way to supplement your water supply. By following proper collection, storage, and filtration practices, you can ensure your rainwater is safe and clean for various uses, including drinking, cooking, and gardening. Embrace this sustainable practice to reduce your environmental footprint and enhance your self-sufficiency.
Do you have experience with rainwater harvesting?
Share your tips and insights in the comments below!
This blog post aims to provide comprehensive information on rainwater harvesting, from collection to filtration, to help readers understand and implement this sustainable practice.
Comments
Post a Comment